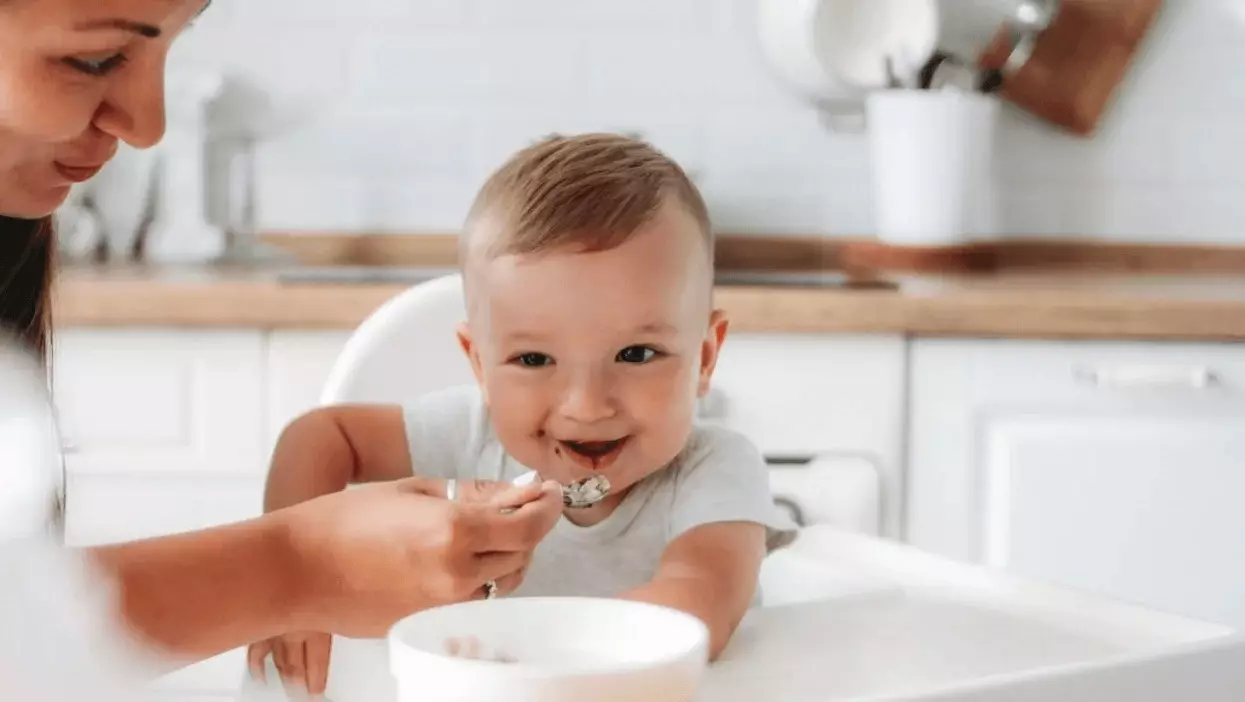
The introduction of solid foods in an infant’s diet is a significant milestone in parenting. However, with the plethora of baby food products on the market, parents often find themselves overwhelmed by choices. Recently, the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee issued its inaugural recommendations for the nutrition of infants and toddlers. This new guidance places a crucial emphasis on avoiding added sugars, which can have adverse effects on children’s health and development.
The Importance of Natural Sugars
One of the central points highlighted in the new guidelines is that while natural sugars, found in fruits and breast milk, are beneficial for infant growth, added sugars should be strictly avoided. Foods like apples and bananas provide essential nutrients and energy vital for cognitive development. The committee clarifies that the focus should not be on eliminating sugar entirely but rather steering clear of artificially added sugars that are prevalent in many processed foods, including sugary drinks and snacks.
The report presents a compelling argument that the first 1,000 days of life—spanning conception through the child’s second birthday—are critical for establishing healthy eating habits. Taste preferences developed during this period can influence dietary choices later in life. By preventing exposure to added sugars during these early stages, parents can help children cultivate a palate for more nutritious food options.
Numerous studies indicate that early exposure to added sugars can potentially lead to health risks later in life. The Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee warns that many infants and toddlers unknowingly consume added sugars, with infants averaging about one teaspoon daily, and toddlers consuming significantly more. Although parents often associate healthful eating with fruits and vegetables, they might overlook added sugars found in various kid-friendly foods, such as flavored yogurts and cereals.
These added sugars not only increase the calorie count of foods but also decrease the intake of vital nutrients. This nutritional displacement can increase the risk of deficiencies, leading to a cycle of unhealthy eating patterns over time. The committee pointed out that nearly 70% of added sugars in the average diet stem from five specific food groups: sweetened beverages, desserts, candy, sweet snacks, and breakfast cereals. This insight underscores the need for vigilant evaluation of nutritional labels before purchasing food products.
Parents must be proactive in avoiding common dietary pitfalls that can introduce excessive sugar into their children’s diets. Simply opting for “child-friendly” versions of food without checking for added sugars can lead to unintended consequences. Juices and snacks that seem healthy often contain significant levels of sweeteners that are detrimental to young diets. Consequently, it’s critical for parents to adopt a habit of reading ingredient labels meticulously.
The guidelines make it clear that babies do not need juice, cookies, or sugary treats as starting points for their diets. By fostering a healthy eating environment, parents can counterbalance societal pressures that glamorize sweet-tasting foods. Instead, focusing on whole fruits, vegetables, and homemade purees can provide babies with all necessary nutrition without the hidden pitfalls of added sugars.
To ease the transition into a healthier feeding routine, innovative companies are stepping up to support parents. Products that feature organic meal options tailored for infants are becoming increasingly popular. For example, meal kits designed specifically for babies, containing no added sugars and rich in nutrients, are ideal solutions. Such offerings can help simplify meal preparation for parents while ensuring their babies receive balanced nourishment.
Furthermore, feeding tools that promote independence and minimize mess have also gained traction. Ergonomically designed utensils, bibs, and cups can enhance mealtime experiences for toddlers and foster important self-feeding skills. These products not only make feeding easier but encourage exploration and enjoyment of nutritious foods.
The new Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee’s recommendations signify a step forward in ensuring the health and well-being of infants and toddlers. By avoiding added sugars and promoting natural, nutrient-dense foods, parents can lay a solid foundation for their children’s lifelong eating habits. As we collectively strive to offer our youngest members a healthy start, it is vital that we stay informed and proactive in our food choices.