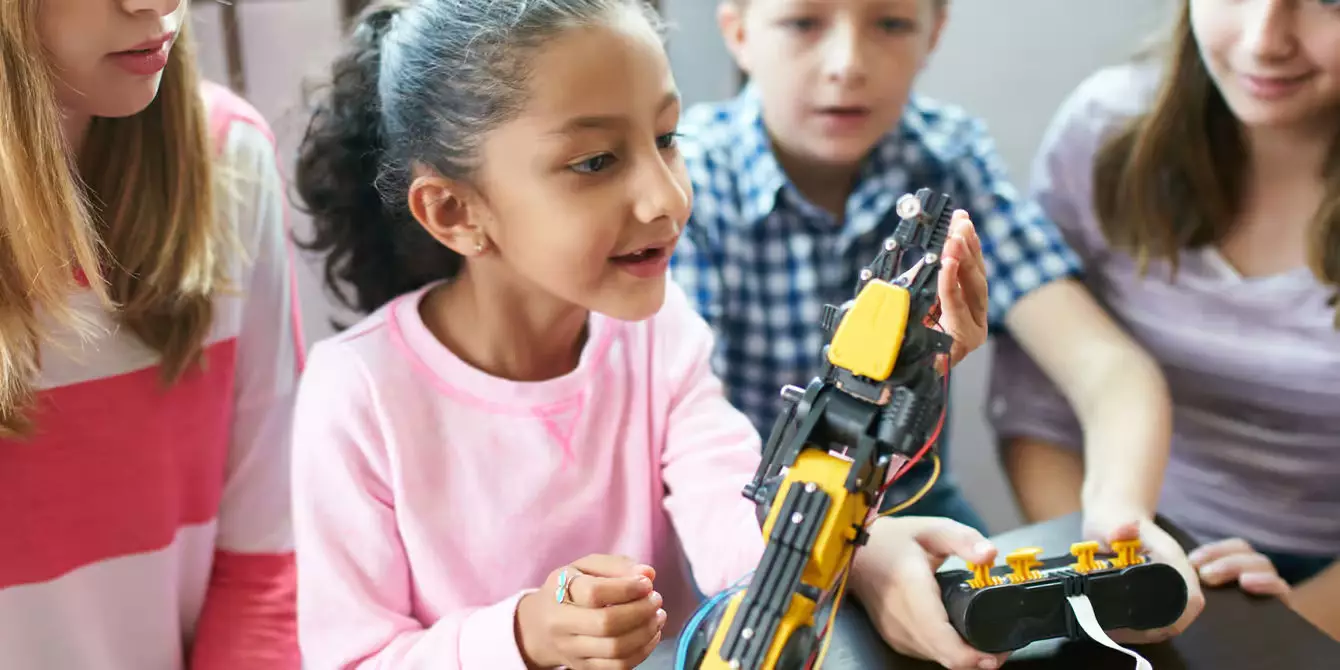
STEM, an abbreviation for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, represents a significant shift in how education is approached in these vital fields. Beyond being just a trendy term, STEM education has been shown to enhance critical thinking, inspire curiosity, promote cognitive growth, and foster creativity among students. The concept of STEM education gained visibility in 2001 when Judith A. Ramaley, then director at the National Science Foundation (NSF), emphasized the necessity of integrating these disciplines into K-12 education. The goal was to cultivate innovative thinkers ready to tackle the challenges of a rapidly evolving workforce, regardless of whether they pursue higher education.
Today, many educational institutions worldwide have embraced the principles of STEM, underscoring its profound role in preparing students for future success. As Dr. Karen Aronian, an education design expert, points out, early childhood is a critical period for introducing STEM concepts. The experiences offered through STEM education can lay a substantial foundation for lifelong learning.
STEM education is built on a hands-on, experiential learning framework that blends its four integral components. Science involves the exploration of nature and its phenomena through observation and experimentation. Technology refers to the inventiveness and application of tools and techniques for problem-solving. Engineering encompasses applying scientific knowledge to create structures, systems, and solutions. Finally, mathematics provides essential reasoning and quantitative skills necessary for analyzing and understanding various situations.
This comprehensive framework encompasses a wide array of activities, from robotics and coding to hands-on crafts like woodworking and sewing. It is imperative to recognize that STEM education does not merely focus on academic skills; it also promotes critical social skills such as collaboration and creativity.
The Benefits of STEM During Early Childhood
Introducing STEM education during the formative years of early childhood can lead to an array of advantages. Educators like Greg McDonough, who oversee STEM curricula, emphasize that children exposed to STEM concepts show improved cognition, memory, and language development. This educational approach provides opportunities for hands-on experiences with manipulatives, such as blocks and tools, which refine motor skills and cognitive abilities.
Moreover, engaging with STEM materials also encourages problem-solving and resilience. Children learn to navigate challenges while gaining confidence in their abilities through trial and error. This is particularly important in early childhood, where the foundation for future learning and exploration is established.
As children mature, the integration of STEM education becomes increasingly relevant. For instance, older students may engage in practical applications like constructing models to demonstrate their understanding of mathematical principles, a departure from traditional testing methods. Such interactive learning experiences serve not only to teach concepts but also to inspire creativity and critical thinking.
Parents can significantly impact their children’s engagement with STEM by fostering a positive, exploratory environment. Emphasizing open-ended questions during play, encouraging independent problem-solving, and creating spaces for hands-on creative activities are vital components of this approach. Developing a ‘maker corner’ stocked with assorted materials can inspire creativity and innovation.
Moreover, introducing STEM-related challenges based on stories or real-life situations can encourage children to devise and build solutions. This method not only makes learning fun but also directly ties academic concepts to familiar contexts, thereby enhancing retention and understanding.
Parents should also consider enrolling their children in STEM-focused preschool programs or extracurricular classes. Such settings are designed to maximize engagement with STEM concepts, ensuring children develop a solid grounding in these vital areas. Additionally, involving children in everyday tasks—like cooking, gardening, or home repairs—allows them to relate STEM knowledge to real-world applications.
As economies worldwide continue to evolve, the demand for a skilled workforce in STEM fields rises correspondingly. Preparing children for these roles begins in early education. Research suggests that early exposure to STEM principles can considerably impact a child’s academic trajectory. The consistent nurturing of curiosity and complex problem-solving skills can lead to long-term success, both academically and professionally.
STEM education is more than a curriculum; it is a pivotal part of a child’s overall development. By encouraging exploration, creativity, and analytical thinking, we set the stage for future innovators and leaders in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Embracing and facilitating STEM from an early age will empower our children to navigate and shape the world that lies ahead.