Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) has recently featured prominently in public health discussions, particularly as we reflect on the peak season noted by authorities like Mandy Cohen, the CDC Director. Though the overall incidence of RSV cases in the United States reached its climax in December 2023, health experts continue to emphasize that the virus remains a significant concern, particularly for vulnerable populations such as infants, especially those with pre-existing health conditions. This article delves into what RSV entails, its impacts on infants, and highlights breastfeeding as a potential protective measure against serious complications related to the virus.
RSV is a common respiratory virus that typically manifests with mild symptoms resembling those of the common cold. In healthy infants and children, symptoms often subside within a week or two. However, RSV can escalate into more severe illnesses, such as bronchiolitis or pneumonia, particularly in premature infants or those with chronic illnesses. Hospitalization statistics reveal a concerning reality: about 1-2 out of every 100 infants under six months may require hospitalization due to RSV complications. This statistic underscores the importance of safeguarding vulnerable infants during RSV season.
As healthcare professionals strive to provide the best possible protection for infants, the shortage of the RSV vaccine for infants remains a noteworthy challenge. Parents of at-risk infants navigate this gap in preventive care, searching for alternative strategies to bolster their baby’s immune defenses.
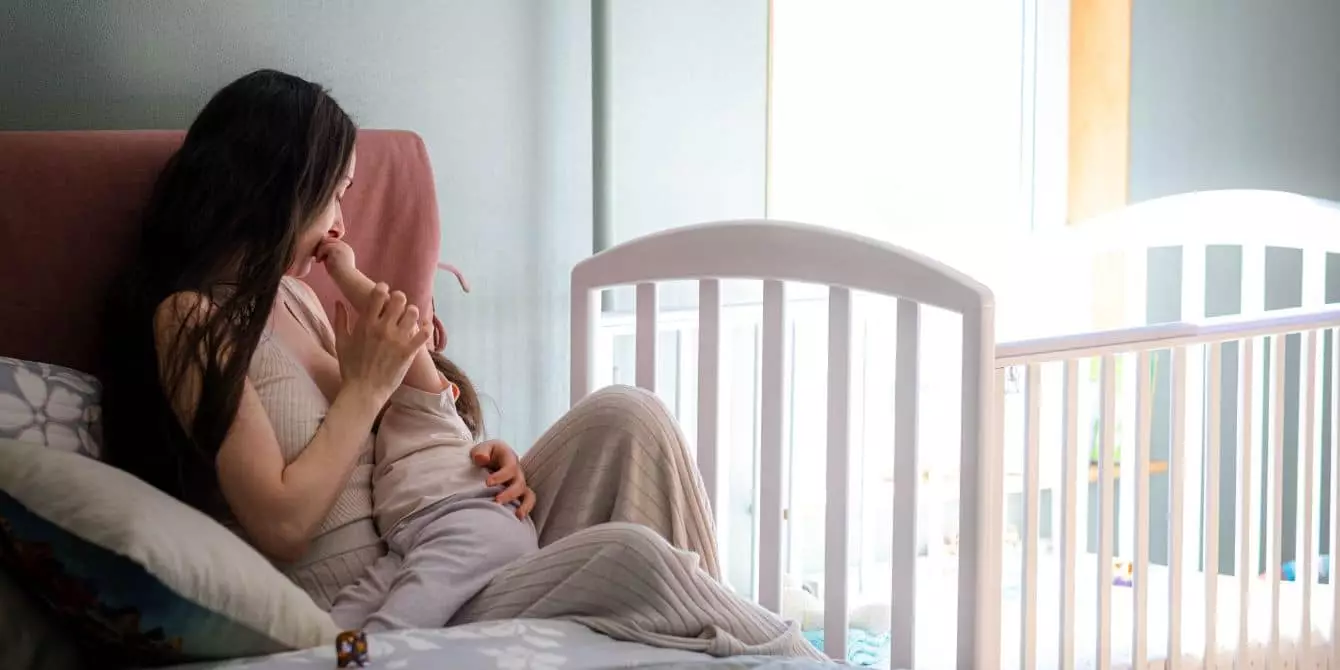
Emerging research indicates that breastfeeding may provide significant immune support to infants, particularly against severe forms of RSV. According to Dr. Jessica Madden, a specialist in breastfeeding medicine and infant feeding, human milk contains critical components including antibodies, lactoferrin, white blood cells, and various vitamins that collectively enhance an infant’s immune functioning. While the World Health Organization advocates for exclusive breastfeeding for the initial six months for optimal immune benefit, many families may face circumstances that prevent this ideal scenario. Nonetheless, even partial breastfeeding combined with formula feeding can yield positive health effects during RSV season.
Multiple studies corroborate the advantages of breastfeeding, with a systematic review published in the journal *Pediatrics* revealing an association between breastfeeding and lower hospitalization rates due to RSV bronchiolitis. Initial findings suggest that infants exclusively breastfed for at least four months showcased especially noticeable protection against severe RSV illness, although even short-term or partial breastfeeding exhibited benefits in reducing the severity of symptoms, the duration of hospital stays, and the need for supplemental oxygen.
Caregiving during an RSV infection demands extra consideration and adaptability, particularly surrounding feeding due to congestion and respiratory difficulties. Dr. Madden provides valuable recommendations for aiding babies who are grappling with RSV symptoms. For instance, parents might recall the early days of cluster feeding, which can also be beneficial during RSV. Infants may find it easier to manage shorter, more frequent feeding sessions to remain hydrated and nourished.
Another practical approach includes utilizing saline nasal drops followed by gentle suction to alleviate nasal congestion, thus easing the feeding process. Creating a steam-filled environment during feedings can further assist in relieving respiratory distress, and ensuring a humidified atmosphere while the infant sleeps can provide ongoing comfort.
During this challenging time, it is crucial that breastfeeding mothers also prioritize self-care, including adequate rest and hydration. A well-rested and healthy parent can enhance milk supply while decreasing their susceptibility to colds and other infections.
As RSV seasons evolve, awareness and proactive measures become vital in protecting at-risk infants. Breastfeeding emerges as an invaluable intervention that not only nourishes but also fortifies the immune system against opportunistic viruses. While challenges such as the vaccination shortage persist, the focus on supportive feeding strategies can help parents navigate the unpredictable terrain of RSV. By prioritizing their health and providing appropriate support to their little ones, families can foster resilience during this critical time.
As we continue to understand the myriad benefits of breastfeeding, ongoing research is essential for developing effective strategies in RSV prevention. Collaboration between parents, healthcare providers, and researchers will pave the way for healthier futures for our youngest and most vulnerable.